envoy-xds-controller
Architecture: Envoy XDS Controller
Architecture Overview
This document describes the internal architecture of the Envoy XDS Controller. For a general project overview, see the Overview document.
The Envoy XDS Controller architecture follows a Kubernetes controller pattern with an embedded xDS server. It consists of several key components that work together to transform Kubernetes Custom Resources into Envoy proxy configurations.
High-Level Architecture Diagram
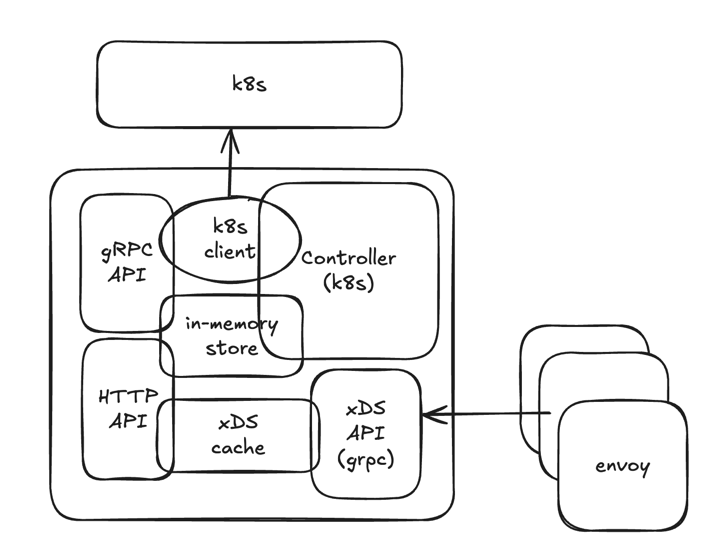
Logical Architecture Components
1. Kubernetes Controller Manager
The main component that manages the lifecycle of Custom Resources and ensures their processing. It includes:
- Resource Controllers - process CR changes and update the xDS cache
- Webhooks - validate CRs before their creation/update
- Health/Readiness checks - provide monitoring of the controller’s state
2. API Definitions (CRDs)
Custom resource definitions that represent Envoy configuration:
- Cluster - defines upstream clusters for Envoy
- Listener - defines listeners (ports and protocols)
- Route - defines routing rules
- VirtualService - combines Listener, Route, and Cluster to create a complete service configuration
- VirtualServiceTemplate - templates for VirtualService
- AccessLogConfig - access logging configuration
- HttpFilter - HTTP filters for Envoy
- Policy - security and access policies
3. xDS Server
Server implementing the xDS API for Envoy:
- SnapshotCache - stores the current configuration for each Envoy proxy
- CacheUpdater - updates the cache when CRs change
- ResourceBuilder - transforms CRs into xDS resources
4. Store
In-memory resource storage:
- Stores all CRs loaded from Kubernetes
- Provides fast access to resources for building configuration
5. API Servers (optional)
API servers for debugging and management:
- HTTP API - REST API for viewing and managing configuration
- gRPC API - gRPC API for programmatic configuration management
6. FileWatcher
Component for tracking changes in configuration files:
- Monitors file changes and updates configuration
Component Interactions
- CR Change Processing Flow:
- Kubernetes API Server notifies the controller about CR changes
- The corresponding controller (e.g., VirtualServiceReconciler) processes the change
- The controller calls CacheUpdater to update the configuration
- CacheUpdater uses ResourceBuilder to transform CRs into xDS resources
- CacheUpdater updates the SnapshotCache
- Envoy proxies receive the updated configuration via the xDS API
- Interaction with Envoy:
- Envoy proxies connect to the xDS server
- The xDS server provides configuration from the SnapshotCache
- When the configuration changes, the xDS server notifies Envoy
- Resource Validation:
- Webhooks validate CRs before their creation/update
- CacheUpdater checks the correctness of the configuration when updating the cache
Technical Features
- Use of controller-runtime:
- The project is built on the Kubernetes controller-runtime
- Uses standard patterns for developing Kubernetes operators
- Extensibility:
- Modular architecture allows adding new resource types
- Support for templates for configuration reuse
- Security:
- TLS support for xDS API
- Integration with Kubernetes RBAC
- Resource validation through webhooks
- Debugging and Monitoring:
- API for viewing current configuration
- Prometheus metrics
- Health/Readiness checks